Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
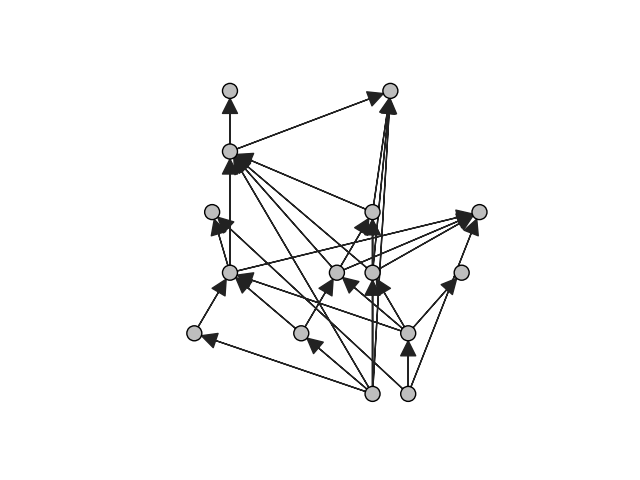
Directed Acyclic Graph
This example demonstrates how to create a random directed acyclic graph (DAG), which is useful in a number of contexts including for Git commit history.
import igraph as ig
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
First, we set a random seed for reproducibility.
random.seed(0)
First, we generate a random undirected graph with a fixed number of edges, without loops.
g = ig.Graph.Erdos_Renyi(n=15, m=30, directed=False, loops=False)
Then we convert it to a DAG in place. This method samples DAGs with a given number of edges and vertices uniformly.
g.to_directed(mode="acyclic")
We can print out a summary of the DAG.
ig.summary(g)
IGRAPH D--- 15 30 --
Finally, we can plot the graph using the Sugiyama layout from igraph.Graph.layout_sugiyama():
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ig.plot(
g,
target=ax,
layout="sugiyama",
vertex_size=15,
vertex_color="grey",
edge_color="#222",
edge_width=1,
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.437 seconds)